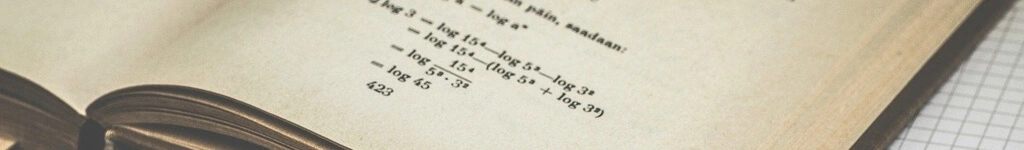In this blog post, we're going to talk about net premiums in insurance. We'll explain what they are, how to calculate them, and even walk you through some practical exercises using Python with real-life examples.
While we touched upon the concept of net single premiums in a previous discussion about …